Info-Cafe
Results for : All categories
Results for : All categories
20 Best Small Business Ideas to Start With Low Investment

One of the various small businesses that you can start with very little investment is a personalized and customized gift store. In fact, this is a hot business idea right now considering how people want to buy such presents for their near and dear ones as well as others that matter in their lives. If you are thinking to start a choicable business, here you can look over some small business ideas can turn your mind to put a thumb for new initiative.
Gym or fitness centre
You can easily start a gym or fitness centre considering how conscious people are these days about fitness. Almost everyone you see out there wants to be fit. So, in case you had some room you could easily start a fitness centre or gym over there and earn good money in the process.
Event management
You could easily start a small event management company that would organize different kinds of events. More than money what you need over here is sufficient manpower and significant amount of expertise in the industry.
Interior designer
These days everyone wishes his home to be decorated by an interior designer or decorator. So, you could easily start that business. However, you need to be trained and certified in order to enjoy a successful career here.
Small grocery shop
Yet another good small business idea with little investment is a grocery store. Here you do not need any special skill as such and you can go on expanding even as you go.
Ice cream parlour
If you have little money then you can do worse than start an ice cream parlour.
Photocopies and book binding
There are plenty of school and college areas that may not have this facility. You can easily fill this gap in those areas and it does have the potential to help you earn.
Mobile food shop
This is the mobile generation. So, it might make sense for you to start a mobile food service such as a food truck.
Making jewellery
The price of gold is always increasing and there is great demand for golden jewellery as well. This is why you can undertake a course in this regard and start a small business that could one day grow into something so much bigger.
Insurance consultant
It is also a good business idea to start a small insurance company of your own or even become the agent of an established insurer.
Freelancer
If you are good at what you do and have sufficient experience and repute in the industry where you work at present you can always consider working as a freelancer.
Book store
You can always count on book lovers to buy several books at once and this is why the idea of starting a book store happens to be such an attractive one.
Catering service
These days, people always look for good catering service for special occasions such as parties and marriage ceremonies. So, if you are skilled in this area then it is one business that you should definitely try.
Computer trainer
If you are capable of providing computer training then this is one business that you would enjoy. In any case, in the modern world it is important to know computers.
Yoga centre
These days life is rather stressful and a lot of people like to practice yoga to stay fit and de-stress. So, in case you are trained in that regard you can jolly well start a new business.
Baby sitting services
This business idea is meant primarily for women who wish to do some home based work instead of moving outdoors for work. You will find a lot of working couples who would be more than willing to avail your services.
Real estate consultant
Real estate is one business that is always growing and as such you can always start a consultancy in this particular industry. You can guide people how to sell, buy, and rent property.
---------------------------------------------------------------
Also Read:
Why to Setup a Business in Bangalore?
Implication of GST on Financial Transactions

The financial transactions are the very center of economic activity as investment in assets, goods and productive activity is funded by financial transactions. These transactions take various forms – from equity to loans, to investment in various securities. Besides primary financing transactions there are numerous secondary market transactions – including traders in securities, assignment and securitization of loans, etc.
The introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) is admittedly one of the most outstanding tax reforms since Independence and therefore, it is very important to unravel the implication of GST on financial transactions. This article is limited to GST on basic financial transaction excluding insurance, stock broking services, etc.
What about GST on Lending Transactions
One of the primary facts one should note while evaluating the applicability of GST is the nearly-all-pervasive nature of the levy. The charging section [Sec 9 of the CGST Act] imposes the tax on any “supply”. Exclusions are items like non-taxable supplies [for example, alcohol for human consumption], or exempt supplies, or supplies which are zero-rated. Hence, the focus shifts to the ambit of the word “supply”, which consists of all forms of supply of goods and services under Section 7 (1) of CGST Act, 2017. Since the word is intrinsically connected with the words “goods” and “services”, one needs to examine the meaning of those terms.
“Goods” are defined in Section 2 (52) to include any movable property, other than money and securities. “Services” are defined in Section 2 (102) to mean anything other than goods, money and securities but includes activities relating to the use of money or its conversion by cash or by any other mode, from one form, currency or denomination, to another form, currency or denomination for which a separate consideration is charged.
Mere money is excluded from both goods as well as services. When read with the word “supply”, supply of money is neither a supply of goods, nor a supply of services. However, Section 2 (102) includes, in the definition of “service”, any activity relating to use of money, even though supply of money itself is not a service. Mere supply of money could be settlement of a transaction – for instance, making a payment for goods and services. It could not have been argued that the person making the payment itself is making a supply. Therefore, the intent of the law excluding supply of money, but including any activity pertaining to the use of money becomes intriguing. This conundrum was faced by the Delhi High Court in Delhi Chit Fund Association Vs. Union of India1 while interpreting similar expression used in sec 65B (44) of the Finance Act, 1994 – the High Court expressed its perplexity in the following words: The Explanation, therefore, seems to offer a clue to the problem which appears to us to be a creation of the very confounding manner in which the definition is found to have been drafted. However, we have to make sense of what we have.
Can it, therefore, be argued that lending of money is an activity pertaining to use of money? If the settlement of a supply in form of a monetary payment cannot itself be taken to be a supply, then, what else could be the exclusion of monetary transactions in both the definition of “goods” as well as “services”, except lending or deposit of money?
The list of exempted services [item 8- extending deposits, loans or advances in so far as the consideration is represented by way of interest or discount (other than interest involved in credit card services)]. That is to say, there is a clear exemption for extending of deposits, loans or advances, insofar as the consideration is interest or discount. Therefore, it does not practically matter whether lending of money is a supply of services or not. However, the question becomes crucial from at least 2 viewpoints:
• Lending of money is a supply of service, but an exempt service in terms of Item 8 of Exemption list
• Interest involved in credit cards is not a fully exempt service
The exemption for financial transactions in India is quite narrow – it is only the interest/ discount earned or paid for loans, deposits or advances. Therefore, if the transaction deviates from a plain vanilla structure and therefore, fails the test of being a “loan”, “deposit” or “advance”, or the consideration is not an interest or discount, the exemption is lost. As a result:
• All earnings and charges other than interest or discount will be chargeable to GST. This includes any upfront or regular charges such as processing fees, documentation charges, service charges, collection charges, inspection charges, repossession charges, foreclosure or prepayment charges and so on.
• If the transaction does not fit into the meaning of “loan”, “deposit” or “advance”, even if the transaction is intrinsically a financial transaction, it does not seem that the supply will be exempt from GST. Thus, if an inventory repurchase transaction or a financial lease transaction may have the substance of a financial transaction, but it will be difficult to contend that they avail the exemption given in Item 8 of the Exemption list.
• Nevertheless, if the transaction is a loan transaction, there is no question of GST on the recovery of principal lent as the tax can only be on the consideration and not for principal recovery.
Is Registration Required Under GST Law for Money-Lenders?
Loan transactions are currently originated from banks, but by thousands of non-banking financial entities, thousands of money-lenders and entities occasionally engaged in lending activities. Therefore, a pertinent question is, is registration under GST law relevant for an entity even though the entity may be earning income by way of interest.
Notably, interest on loans is exempt as per the exemption discussed above; however, the registration requirement is based on (a) aggregate turnover in a financial year exceeding Rs 20 lakhs and (b) the supplier making a taxable supply. The term “aggregate turnover” as defined in Section 2 (6) includes value of all exempt supplies as well. Thus, while there is no GST on interest on loans, but the same is still captured in while computing aggregate turnover. Thus:
• If the aggregate amount of turnover (note that this is all – India turnover), including interest, in a year exceeds Rs 20 lakhs and
• The entity has received any consideration other than interest (any amount whatsoever) or made any other taxable supply (for example, even sale of scrap in the office), the entity will require registration.
Companies Limited by Shares vs. Limited by Guarantee

When you are going to setup a new limited company; before that you must have to take a decision on company category type. However, the company category is classified into two types such as
- Company limited by shares: Nowadays, most of the companies are moving for Limited by Shares; this type is likely to be opted for commercial nature of business for profit making organization
- Company limited by guarantee: This type company is likely to be opted for non-profit businesses like community and charitable trust organizations
While you're planning to setup a company, it is your wish to choose the perfect type, whether it may be limited by share or limited by guarantee; it is depends on your future vision and nature of business.
Company Limited by Shares
A company limited by shares can be described as an incorporated business structure and is regarded as a legal person or entity, which is held responsible for its own debts. It is the most popular company structure out there and is normally created by people who wish to earn profits from their business ventures.
The biggest advantage of such a company is that it can be started by any business irrespective of its size and this includes startups as well. It can be owned by at least one person or more. These owners are also referred to as member or shareholders. In order to become a shareholder you should have at least one share in that particular company.
In these companies the shareholders enjoy a limited amount of liability. In case the business in question becomes insolvent a shareholder would only need to pay the price of his shares. Beyond that the company itself would be held responsible for all the debts incurred by itself. In these companies the shareholders get shares of the profits made by the business. This is proportionate to the amount of shares held by them or the percentage of the same with respect to the total shares offered by the company.
The owners of the company appoint managers in order to look after the daily activities of the company. In most cases the shareholders employ themselves as the directors of such a company.
Companies Limited by Guarantee
The company limited by guarantee doesn't have share capital as per Companies Act. This company constituted with Guarantors and they're called as Members. And the company is treated as separate legal entity from its members.
As far as legal definitions are concerned both the companies are one and the same. However, the ownership pattern of these companies is different in the sense that there are no shareholders.
In these companies, the owners are also referred to as guarantors. They can be called members as well. Anyone can become a guarantor by assuring to provide a certain sum of money to the company in question.
The money guaranteed is the extent to which someone is held liable towards the business. It needs to be paid when a company goes out of business.
Here too, directors are appointed by members in order to take care of the everyday affairs of the company and as is the case with most companies limited by shares here too the guarantors themselves become the directors.
Difference between Company Limited by Shares and Limited by Guarantee
However both two company types are different from each other in terms of profit distribution, but both provides a common advantage on company formation i.e. limited liability to the members.
Here you can take a look to the clear, concise and close comparison between companies limited by shares and limited by guarantee:
|
Sl. no |
Basis of Distinction |
Limited by Guarantee |
Limited by Shares |
|
1 |
Definition as per the Companies Act, 2013 |
“Company Limited by Guarantee” means a company having the liability of its members limited by the memorandum to the amount as the members may agree by contract to bestow the assets of the company in the event of its being wound up. [As per Section 2(21)] |
“Company Limited by Shares” means a company having the liability of its members limited by the memorandum to the amount, if any, unpaid on the shares respectively held by them. [As per Section 2(22)]. |
|
2 |
Meaning- Required as to Memorandum |
Memorandum states that members shall have limited liability to the extent of the amount that they have guaranteed to pay to the company at the time of its winding up. |
Memorandum states that members shall have limited liability to the extent of the amount unpaid, if any, on the shares held by them. |
|
3 |
Object |
They are formed to provide specific services to the public and are non-profit making business. Therefore, it has specific objects & detailed rules pertaining to which areas they want to work upon. |
They are formed for profit-making business and have very general objectives and the clauses which allow them to pursue any legal activity or trade. |
|
4 |
Share Capital |
May or may not have share capital |
Must have share capital |
|
5 |
Shareholders |
There are no shares – hence there are no shareholders. Instead, the company will have members. |
Owners of shares are called shareholders of the company. |
|
6 |
Company |
Companies limited by guarantee are non-profitable organization. They are specially designed for charitable purposes. |
Companies limited by shares are profit making organization |
|
7 |
Examples |
Advanced PCB Technologies Private Limited |
Which one should you choose?
The decision regarding which form of company you should choose depends on the profit sharing model that you wish to follow. This is always going to be the most logical and straightforward approach that needs to be taken in such cases.
If it is a profit-making business that you want you should go for a company that is limited by shares. If you want your company to be a non profit-making one your company should be limited by guarantee.
In case, it is not that simple or making you confusion, then you can talk to a professional business consultant or adviser and find out what you should do. You should be able to get proper guidance from them. In this context you should also remember that you cannot change your company from one form to another.
--------------------------------------------------------
Read On More:
How to Register a Company in Bangalore India?
Difference between LLP and Private Company
Procedure for export and import in India

As far as overall merchandise exports are concerned India ranks 19th in the world. In terms of overall imports it lies at the 12th spot. The present Indian government is said to be in favour of businesses and as such it is expected to sign a number of deals that would make the trade sector much more liberal than it already is. It is expected that in the days to come these trade liberalization deals would make it easier for more import and export related businesses to start in India. However before you start such a business there are a few things that you need to know really well. Documentation is an important part of this business. As the entrepreneur or business owner it is important that you understand this part really well.
The first step
If you wish to do an import and export business in India you need to get an Import Export Code (also referred to as IE Code). This particular code will be provided by the Directorate General of Foreign Trade. You can get this code by providing your PAN and opening a business bank account. There are plenty of websites in India that can help you get the IE Code. If you need a import export code (IEC) license for your business, we can assist you to obtain the IE Code in Bangalore Karnataka or anywhere in India through online.
Commercial invoice
Commercial invoices are issued by sellers to the buyers. They have the terms of transaction such as the date when the transaction happened, details pertaining to sellers, details of buyers, value of the transaction, and terms of shipping to name a few. It is on the basis of the commercial invoice raised by the seller that customs duty is imposed on a shipment.
Airway bills
An airway bill can be regarded as the proof that goods and shipment are being sent by the air. These bills also act as proofs of the fact that the air cargo agent has received the goods that are to be shipped. Such a bill acts as an invoice for the air shipment as well as being a certificate of insurance. It also provides guidance to the air cargo agent regarding how it is going to handle, dispatch, and deliver the shipment in question. Typically, an airway bill would contain details such as information on the consignee and the shipper. It will mention the destination airport as well as the departure airport and describe the goods that are being shipped. It would bear the carrier’s sign and seal as well.
Bill of lading
A shipping agency provides bill of lading for the goods that it has shipped. Such a bill normally has information regarding the shipper, the consignee, the vessel that is carrying the goods, the port where the goods are loaded and one where they are discharged, the place of delivery and receipt, the mode of payment, and the carrier’s name.
Some more important documents in this regard are bill of exchange, certificate of origin, packing list, and letter of credit. A bill of exchange is used when an importer decides that it would pay the exporter at a future date or before it. This date is normally arrived upon by mutual agreement.
----------------------------------------------------------
Related Posts:
How to Start an Import Export Business in Bangalore & Its Procedure
How can I Apply for Shop & Establishment Registration in Karnataka?

No matter what kind of shop or establishment you are opening in Karnataka; you would have to apply for registration with Department of Labour, Karnataka and get the license for your respective business. As per the BBMP (Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike) rules and regulations, you have to acquire this license certificate for running your business in a certain place of Bangalore, Karnataka. It is mandatory for every business.
These days the Karnataka government has made it easy for you to perform these procedures online by starting the e-Karmika portal. This is the online facility where you can register, as well as renew your establishments.
All this is done under the aegis of Karnataka Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, 1961. This particular act just happens to be one of the many State Labour Laws and Rules that the Department of Labour is implementing. And in different places of India, the people know this license as Gumasta license.
Rules and laws to shops and establishments
The department performs a whole range of functions and this includes enforcing a number of laws in the state. As per these laws, the citizens need to interact with the department. All this is part of various enactments of the Indian government as well as the Karnataka government. Karnataka Shops and Commercial Establishments Act, 1962 covers a number of areas where the department is supposed to work.
They may be mentioned as below:
- Issuance of registration certificate
- Filing of annual returns
- Renewal of registration certificate
- Exemption on weekly holidays for shops and establishments
- Amendment in registration certificate
- Exemption for women working in night shift
- Issuance of duplicate registration certificate
- Submission of appeals
What is shop & establishment registration?
Shop and establishment registration means your business is registered under the constituted Law of State labour department through the Senior Labour Inspector in the jurisdiction of your regional circle and your organization will be officially registered in Government record and secured a place for major alteration. But the Department has the authority to monitor the workers working hour’s time, weekly holidays, leave structure for employee and etc. as it is mentioned according to the rule. This is why; you are moving forward one step, towards achieving your business goals.
Who needs to obtain the certificate under the Karnataka Shops and Establishment Act, 1961?
The thing is that any people who are doing their business either as a shop or an establishment, they must have to get the registration from the specific authority of regional labour offices of Karnataka to make secure of his/her organization.
Shop/ Trade license is subjected to state department. And this license is mandatory for all business entities.
So every shop/ establishment needs to register itself with their state labour department within 30 days of commencement.
Here's the following business organizations are required to obtain their shops and establishment’s licenses are:
- Shops
- Commercial establishments
- Restaurants
- Hotels
- Theaters
- Public amusement
- Retail trade
How to determine what is Shops and Commercial Establishment?
Shop: A shop refers to your business or trade which is physically situated on a place where it is providing the services/goods to whom, whether it may sells their goods or services as retailer or wholesaler where services are rendered to customers. It includes all your offices, storerooms, godowns and etc. are in the same building for business purpose but it doesn’t include under the commercial establishment.
Establishment: A commercial establishment is refers to an economic unit or banking sector or an insurance organization engaged in commerce to produces or sells their goods/services from a single location.
A commercial establishment is an establishment refers by the state shop & establishment act to hold on the activities on commercial purpose; which is used to produces or sells their goods/services from a specific location. And such type of activities comes under the establishments such as hotels, restaurants, coffee bar, theater, banking sectors, financial institutions, a cafe are comes under the State Governments Shop and Establishment Act.
Benefits of Shop and Establishment License
The owner of the shops or establishments can get these below advantages by registering of his/her own business entity under the Karnataka Shops and Establishments Rules, 1963.
- The shop and establishment license along with Chartered Accountant (CA) Certificate helps to open a Current Bank Account for your business.
- It helps to get loans easily from Banks or Financial Institutions to expand and grow your business.
- It helps to get the facilities to enjoy the Tax Benefits, Power Tariff and exemption from State Govt.
- It helps to show your shop registration proof when any inspector from State Govt. Labour Department or Municipality visiting to your office premise.
- One another important benefit is that the registration of shop and establishment for obtaining license/ certificate is fully online. You can apply it through the below process with proper documentations, no need to visit again and again to regional jurisdiction.
Documents to be uploaded during the shops and establishments registration
As you would know as a prospective business owner, certain documents always have to be provided at various stages of your existence to relevant authorities. Here too scanned copies of certain documents need to be uploaded at the time of making the application for opening a shop or any other establishment in Karnataka. Those documents may be mentioned as below:
- Proprietor/ Designated or Managing Partner/ Director’s photo
- Identity proof of the owner/ authorized signatory (PAN Card/ AADHAAR Card/ Driving License/ Voter ID)
- Address proof of shop/ establishment with rental or lease agreement
- Authorization letter from authorized signatory/ self attestation letter of owner
- Duly filled Registration Form signed by owner/ authorized signatory
- Challan/ Payment Receipt/ Transaction Receipt
- Statutory documents (BBMP Trade License/ Partnership Deed/ Incorporation Certificate [COI]/ Memorandum of Business [MOA & AOA])
Procedure for Karnataka Shops & Establishment Registration
As per the state rule, every state follows their specific registration process. So, here you can get a brief idea on online application for shops and commercial establishments in Bangalore Karnataka. And for this, you have to follow the steps to acquire the license certificate in Bengaluru or anywhere in Karnataka.
- Go to this site https://labouronline.kar.nic.in/, E-Labour Depratment for online registration/ renewal of shops & establishments license. Here you just move your mouse to APPLY ONLINE menu and click on Shops and Commercial Establishments Act. It will drive you to Government of Karnataka, Department of Labour where you would register your business.
- Click on New Registrations and fill the form online, submit it.
- Username and Password will be generated and send to your mobile number
- Fill and submit the application form online to Chief Inspector of your concerned regional circle office
- Take Challan from any nationalized bank based on your number of employees
- Make attachment of necessary documents along with the Bank Challan
- Get the acknowledgement number
- Submit the physical copy of online application form in the particular regional circle
- After verification by the Senior Labour Inspector, if everything is well; you shall be granted the registration certificate
- Obtain the certificate
Here, look at the list of attachments required for specific organization for obtaining shop & establishment license:
Attachment Required for Private Limited / One Person Company
- COI (Company Incorporation Certificate)
- MOA and AOA
- PAN of the Company
- PAN of the Directors
- Passport size photo of directors
- Address proof of the Directors
- Authorization Letter
- Rental Agreement/Sale Deed/Lease Deed
- Electricity bill for office address proof
- Rental Agreement/Sale Deed/Lease Deed for additional place of business
- NOC (No Objection Certificate)
Attachment Required for Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
- COI
- LLP Agreement
- PAN of the Company
- PAN of the Directors
- Passport size photo of directors
- Address proof of the Directors
- Authorization Letter
- Rental Agreement/Sale Deed/Lease Deed
- Electricity bill for office address proof
- Rental Agreement/Sale Deed/Lease Deed for additional place of business
- NOC
Attachments Required for Proprietorship Firm
- PAN of the proprietor
- Address proof of the proprietor
- Passport size photo of proprietor
- Authorization Letter
- Rental Agreement/Sale Deed/Lease Deed
- Electricity bill for office address proof
- Rental Agreement/Sale Deed/Lease Deed for additional place of business
- NOC
Attachment Required for Partnership Business
- Certificate of firm
- Partnership deed
- PAN of the Firm
- PAN of the partners
- Passport size photo of Partners
- Address proof of the Partners
- Authorization Letter
- Rental Agreement/Sale Deed/Lease Deed
- Electricity bill for office address proof
- Rental Agreement/Sale Deed/Lease Deed for additional place of business
- NOC
Registration Fee Structure of Shop and Establishment in Karnataka
If your company does not have any employee other than yourself, you would need to pay a registration fee of INR 300. In case there are between one and nine employees in your establishment you would need to part with INR 600. In case the number is between 10 and 19 you would have to pay INR 4,000 as registration fee.
In case you have hired anywhere between 20 and 49 employees you would have to pay INR 10,000. The amount would go up to INR 20,000 in case there are 50 to 99 employees in your shop or establishment. If you have 100 to 250 employees you should be paying a registration fee of INR 40,000. If there are between 251 and 500 employees in your unit then the registration fee payable by you would increase to INR 50,000. If the number of employees in your company is between 501 and 1000 the registration fee applicable for you would be INR 70,000. If you have more than 1000 employees you should pay INR 75,000 as registration fee.
Here you can find the chart of registration fee as per the Department of Labour, Karnataka for the number of employees or workers in an organization.
|
Registration Fee |
|
|
No. of Employees |
Fees (Rs.) |
|
No Employees |
300/- |
|
1 to 9 Employees |
600/- |
|
10 to 19 Employees |
4000/- |
|
20 to 49 Employees |
10000/- |
|
50 to 99 Employees |
20000/- |
|
100 to 250 Employees |
40000/- |
|
251 to 500 Employees |
50000/- |
|
501 to 1000 Employees |
70000/- |
|
1000 Above Employees |
75000/- |
How to Check Shop and Establishment Application Status?
To know the position of your application of shop & establishment online in Bangalore Karnataka; you need to follow the two simple tips.
Note: Before going to check the application status, keep the acknowledgement number with you first.
1. Visit this web page http://164.100.133.176/ekarmika/UserCredentials/Status.aspx; this will be open like the below screenshot. See the specified image below:
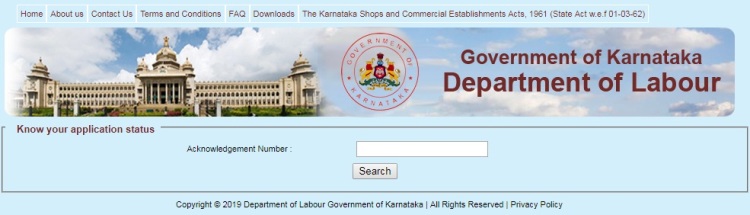
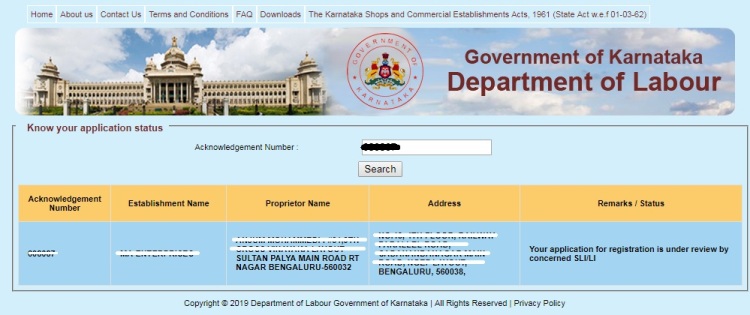
2. Enter your application Acknowledgement Number in specified field and click on “Search” button. A new window will open and display your Acknowledgement Number, Shop or Establishment Name, Proprietor Name, Address and Remark/ Status as shown by the below screenshot. And you will able to know the status of your application.
How to Verify Shop and Establishment License Certificate?
Why a proprietor or business owner wants to know about his/ her license?
To check the certificate license is correct or not.
Because he/she should ensure that I've registered my shop or establishment and got the real legal certificate for running the business.
To verify your shop or establishment certificate license online in Bangalore Karnataka; you’ve to browse the Department of Labour, Govt. of Karnataka website and find in this way.
Here you've to follow the 2 simple steps:
1. Go to this http://164.100.133.176/ekarmika/UserCredentials/CertificateView.aspx web page, you will get a new window as shown in below screenshot.
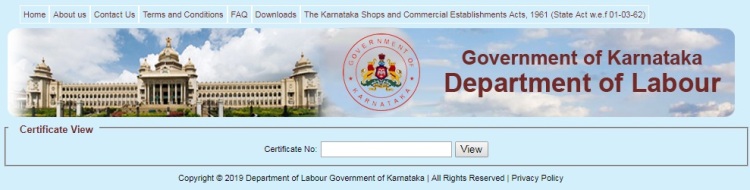
2. Enter the Registration No. in empty Certificate Number field and click on “View” button. This will display your Establishment or Shop Name, Acknowledgement and Certificate Number, View Certificate in a tabular format as shown in below screenshot.
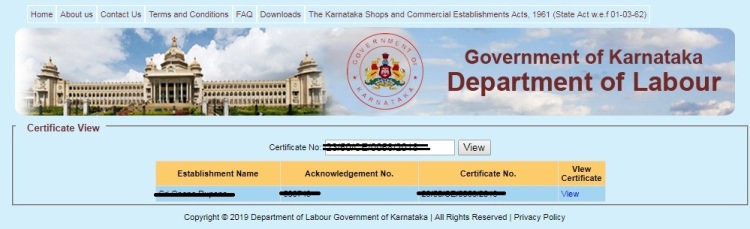
And here you can download the certificate by clicking only on “View” link just down to view certificate and get the detail information of it and keep it for future legal purpose.
Required Renewals in Time
You need to renew your shop & establishment license in a 5 years term basis, i.e. renewal once a 5 year. Remember before one month of your certificate expiration, you need to apply for renewal.
Note: The users who have already taken registration online, they can use the same Username and Password for Renewal, Amendments, Closure and Annual Returns.
While Making Any Changes in Office
Changes can be done as when you required to make change like the office address, changes of director/proprietor/partner, addition place of business, etc.
If you're changing something in your busnines, you've to intimate the department and update your details with respect to the business; which help your customers know all about your business changes with regards to company and also avoid legal actions from the state authority.
----------------------------------------------------------------
Related Articles:
How to Start Import Export Business in Bangalore and Its Procedure
How to Get MSME Registration Certificate in Bangalore Karnataka?
How to Get FSSAI License in Bangalore Karnataka?
How to Claim Income Tax Refund: A Step by Step Guide
Difference between Registered and Unregistered Trademarks

There are several areas of difference between a registered and an unregistered trademark. At the very basic level they differ in terms of the protection that they offer to their respective owners. A registered trademark can be described in legal jargon as a statutory remedy and the latter can be regarded as a common legal remedy.
In case of registered trademarks it is very important that you are able to establish the fact that an infringing mark is exactly, or at least highly, similar to your trademark as that will help establish the fact that there has been an infringement of sorts.
The thing with unregistered trademarks
The thing with unregistered trademarks is that you may get some protection from them but this is only applicable when the product or service in question enjoys a significant position in the market that it is operating in. It is very important that your common buyers are aware that such a trademark belongs to you. These trademarks also differ from one another in terms of the signs that represent them.
A registered trademark is represented by ® and an unregistered trademark is represented by ™, which stands for the trademark symbol.
Laws related to trademarks
The laws related to trademarks tend to differ from one country to another. For example, in India you have Trademarks Act. It may also be that in a particular territory it is not obligatory for you to register your trademark like it happens in India. It needs to be said that in this particular respect India differs significantly from so many other countries of the world.
In India, an unregistered trademark is also granted protection and it comes with several benefits as well. However, as you would know, the matter of statutory right of infringement is not applicable to an unregistered trademark like it happens with a registered trademark. This is the reason why it is always better to get your trademark registered because of the benefits that come with it and the value that it has.
Advantages of a registered trademark
There are several advantages that you enjoy when you register your trademark. For starters, you have a whole host of exclusive rights. This includes the right to exclusive use of the trademark in question for your products and services.
Normally, you need to register a trademark for a decade and then keep on renewing it. The process of registration is governed by various laws for such purposes in different countries.
In India, this is done by Trademarks Act 1999. There are certain reasons as to why you should get your trademark registered. For business organization, it helps your goods and services to be identified and distinguished from those of your competitors.
You can also advertise your goods and services in an effective way by using your registered trademark. It also plays a major role in keeping your commercial goodwill safe.
The most important thing of all is that if a buyer is aware of your trademark he will not buy any substitute product or service that is nowhere as good as what you offer.
Let’s take a look on brief comparison chart of registered and unregistered trademark and know how they are differentiated from each other.
|
Registered Trademark |
Unregistered Trademark |
|
Registered trademark is a hallmark/legal mark for a brand, logo, symbol or design which is legally registered under the Trade Marks Act, 1999. |
An unregistered trademark is a trademark which is not registered under the Trade Marks Act, 1999 and does not have the rights/safeguards against contravention. |
|
Registered trademark is represented by the symbol (R) |
Unregistered trademark is symbolically represented as (TM) |
|
Registered trademark possesses a statutory right of infringement |
Unregistered trademark does not possesses the statutory right of infringement |
|
It has the rights to take legal protection against the piracy or misuse of your brand. |
But, it does not get much protection & cannot stop a third party from using the same mark |
|
The owner of the business can use the TM symbol once they applied for trademark and he has the right to legal protection |
In case of this, proprietor can use TM symbol but has no right to use the R symbol |
|
According to Section-28 of the Trade Marks Act, 1999, trademark registration secures the goodwill of the trader and gives protection to brand name |
As per Section-27 of the Act, no action can be taken for infringement in case of unregistered trademark |
|
In registered trademark, you use R symbol to get the name and fame for your products or services legally |
In unregistered trademark, you can use the symbol TM to signify your products from others but does not have security and legal protection as compared to registered trademark |
In a legal point of view; we suggest that getting trademark for your business is beneficial which helps to take actions on piracy and also protect your brand name, logo, slogan, and etc. from being duplicated by others. This trademark creates a high brand value, earns trust & credibility and consumers can rely on products/services. So it’s better to do trademark for your business to avoid the loss of organization’s familiarity and business.
In BusinessWindo, we provide cost effective and efficient company incorporation services as well as all taxation and legal service solutions regarding to company registration in Bangalore Karnataka or anywhere in India.
---------------------------------------------------------------
Related Post:
Difference between Trademark, Copyright and Patent

Before you seek to understand the differences between trademark, copyright and patent, you need to know the concepts of trademark, copyright & patent which are very important that you comprehend what they are. Then you can go for valid difference points.
First we've to understand it, that these three things are considered as intellectual property. And any person or organization can acquire it by providing its clear evidence of own creation.
Let's move to the concept of 3 IPR (Intellectual Property Right).
Concept of Trademark
Trademark can be a word, slogan, logo, symbol, and image of a business brand. It is treated as one of the most intellectual property assset of a company. A trademark can be filed by product owners as well as business owners.
Trademarks normally deal with the following components:
- Name
- Word
- Slogan
- Symbol
- Design
- Image
If any one of these is trademarked, then it acts as the signature of the brand or business that has done the trademark work. Its main function is to differentiate a product or a brand from others of its ilk, ones that can be regarded as its competitors.
Concept of Copyright
A copyright is an intellectual property right for a real creator who crafts the material resourcees on literal, musical, artistic, cinematography, computer programs, etc. so that he/she can be eligible to acquire copyright license for its own creation. But remember it should be a unique, new, and fresh and differentiated from others.
Copyright is being used for the protection of following works:
- Authors
- Artists
- Choreographers
- Architects
- Creative professionals
It is true that it is impossible to copyright an idea as such but you can always copyright the tangible form of an idea.
This can and does by including all of the following original works and more:
- Authorship
- Photographs
- Sculpture
- Choreography
- Architectural work
- Sound recording
- Motion pictures
- Different creative work
Concept of Patents
Patent is also an intellectual property right under IPR Act for new creative invention. The innovation could have such values to put a great impact on human life development process.
On the other hand, patents are filed by designers and inventors. With the help of a patent these entities are able to protect inventions that offer new and improved functionality.
Patent can include with the following things such as:
- Machine
- Product design
- Industrial design
- Chemical compositions
- New invention process, as well as the designs for all of these.
Differences Between Trademark, Copyright and Patent
An easy and brief comparison chart on trademark, copyright & patent which helps you get a clear idea on it.
Here's you can take a look at simple distinction between trademarks, copyright and patent:
|
Trademark |
Copyright |
Patent |
|
Gives the owner exclusive use of certain phrases/ images. |
Gives the owner exclusive rights to material resources. |
Gives owner property rights relating to an invention. |
|
Protects a word, phrase, symbol or design that identifies the source of the product. |
Protects works of authorship, published or unpublished protect creative or intellectual works used for:
|
Protects invention of a person or organization so no-one can misuse the same. |
|
Also known as ‘service mark’. It refers to service, rather than a product. |
Considered as territorial or national right for creative work on literary, artistic, educational or musical form. |
Considered as a “property”; therefore it can be bought, sold, mortgaged or licensed by owner |
|
Mostly used in commerce. |
Mostly used in literature, education, entertainment, programming. |
Mostly used in organizations. |
|
Prevents companies from selling a similar product with the same or similar word or symbol. |
Prevents others to use the original expression of an idea from a creative work. |
Prevents anyone from making, using or selling the patented invention. |
|
Duration of trademark is 10 years from registration. |
Duration of copyright is life of the author plus next 60 years. |
Duration of patent is 20 years from date of application. |
|
A form of protection for a brand name. |
A form of protection for a creative work. |
A form of protection for a new invention. |
Difference With Regards to the Benefits of Trademark, Copyright & Patent
Benefits of using registered trademark:
As far as a trademark is concerned it improves the rights of the entity that has filed it by way of making available legal evidence. Benefits of trademark provide a public notice of ownership as well. It acts as sufficient proof of the fact that the owner has exclusive rights to the product or brand mark in a certain nation.
Benefits of using registered copyright:
In case someone infringes the copyright, the owner has the right to sue that particular entity.
The benefits are similar in case of a copyright as well. Here too the owner has legal proof of ownership apart from the fact that the copyright serves as a public notice of ownership. Provided that the owner has the advantages of copyright for the same. He/she can sue a person at a court of law for infringing his copyright.
Benefits of using registered patent:
With the help of a patent an owner is able to prevent any manufacture, sale, usage, and import of the invention that has been protected under the IPR law. He has the exclusive rights in this case.
Difference With Regards to Tenure of Trademark, Copyright & Patent
A trademark has to be renewed every 10 years; means its validity timeline is 10 years. But it does remain valid for a lifetime.
The validity period of a copyright is 60 years excluding with owner's life.
However, in case of a patent the validity period expires at the end of 20 years and it cannot be renewed after that. A provisional patent can be availed for a one year period however.
The biggest thing about these three is that while they are unique for a product, but can have one or more of them at a time.
----------------------------------------------------------------
Related Posts:
How to Apply for Trademark Registration in Bangalore?
Why Trademark Registration is Vital for My Business?
How Trademark is Important for Your Business?
How to Register an IT Company in Bangalore, India

You can form a private limited IT company in Bangalore rather easily. All you need is two members. You can have more than this number but it should never exceed 200 members. It is also important that your company has at least a couple of directors and 15 at the most. In most cases there are three kinds of programmes that service providers in this domain have for such clients. The basic plans normally offer the following facilities:
- Digital signatures
- MOA (memorandum of association) and AOA (articles of association) drafting
- Director identification number (DIN)
- Certificate of incorporation
- Name reservation
- TAN (tax deduction and collection account number) and PAN (permanent account number) for your company
How to form a limited liability partnership (LLP) in Bangalore?
If you wish to form your IT company in Bangalore as an LLP you need at least two designated partners. In these cases however there is no upper limit on the number of partners that may be there. Here too the service providers offer three levels of services – basic, standard, and professional. The basic plans normally offer the following services:
- Digital signatures
- MOA and AOA drafting
- DIN
- Certificate of incorporation
- Name reservation
- TAN and PAN for your company
The standard plans give you all the facilities of the basic plans alongwith professional tax enrollment, and commercial and shop establishment. In the standard plans you have facilities such as Registrar of Companies (ROC) yearly filing for the first year alongwith all the facilities of the basic plans.
How to form a one person company in Bangalore?
You can form your IT company in Bangalore as a one person company too. It is a lot like a private limited company but you can operate it just by yourself. After operating it as such for a couple of years you can change it to a private limited company. This can also be done if your company’s annual turnover exceeds INR 2 crore. Here too the services are divided into three categories – basic, standard, and professional. The basic plans offer the following services:
- Digital signatures
- MOA and AOA drafting
- DIN
- Certificate of incorporation
- Name reservation
- TAN and PAN for your company
How to form a partnership firm in Bangalore?
You can always form your IT company as a partnership firm in Bangalore. In fact, such a company can be formed by one or more people. A partnership firm can be created when all the interested parties sign on the partnership deed. At the basic level these service providers would provide services such as partnership deed, stamp duty, registration certificate, and PAN and TAN for an LLP. In the standard plans you would get services such as shops and commercial establishment, professional tax enrollment, and all the services provided in the basic plans.
How to form a foreign subsidiary in Bangalore?
If your IT company in Bangalore is actually a subsidiary of an international enterprise then you would need at least a couple of directors as well as shareholders. The same also applies to foreign nationals who wish to set up such a company in the city. However, at least one of your directors should be a resident of India. Both the shareholders can be non resident Indians (NRIs) or foreign nationals. In the basic plans for such work you get the following services:
- Digital signatures
- MOA and AOA drafting
- DIN
- Certificate of incorporation
- Name reservation
- TAN and PAN for your company
The standard plans for such incorporations include all the facilities of the basic plans and more such as the following:
- Share certificates
- Minutes of first board meeting
- Statutory register
- Service tax
--------------------------------------------------------------------
Related Posts:
Guideline for Company Registration in Bangalore
Why are most of Entrepreneurs Opting for Private Limited Company?
Advantages of Registering a Private Limited Company in India
What are the Steps to Setup a New Startup Company in Bangalore?
Know Which Items Could Get Cheaper Under GST

The Modi government has changed the tax system of India which has been pending from last 10 years long residency rule and finally GST is rolled out for number of goods and services. This is the biggest tax reformation since Independence will hold the key role of nation’s growth, development and integration if it is implemented properly, will bring transparency in taxation system and put efforts to stand a nation in a good position.
GST is applicable for supply of goods and services to traders, businessman, taxpayer, restaurants, service sectors, etc. and even if to end consumers. So people are thinking which items/product’s tax got hiked under GST regime or decreased their tax as compared to the earlier tax system.
Most of us looking for which products and services get cheaper in recently rolled out GST. Apart from certain items/things/services are completely exempted from tax base, here we are discussing about the diminished tax rate of GST for certain products and services. Items that will have cost low from now days onwards.
Below is a comprehensive list of the goods and services which have become cheaper than the earlier tax rate.
|
SL. No |
Items - Things |
Old Tax Rates (%) |
GST Rates (%) |
|
1 |
Soyabean, Groundnut, Sunflower Seeds |
6 |
5 |
|
2 |
Coffee, Tea |
6 |
5 |
|
3 |
Frozen Vegetables |
6 |
5 |
|
4 |
Sweetmeats |
12 |
5 |
|
5 |
Bakery Mixes, Dough’s, Pizza Bread |
12 |
5 |
|
6 |
Vegetables Fat & Oils |
12 |
5 |
|
7 |
Tea Concentrates, Soups |
12 |
5 |
|
8 |
Handmade Safety Matches |
18.5 |
5 |
|
9 |
Broomsticks |
18 |
5 |
|
10 |
Beet Sugar, Cane Sugar |
26 |
5 |
|
11 |
Steel Utensils |
18.5 |
5 |
|
12 |
LPG for Domestic Supply |
17 |
5 |
|
13 |
Household Copper Articles |
18.5 |
5 |
|
14 |
Copper Utensils |
18.5 |
5 |
|
15 |
Iron / Steel / Household Articles |
18.5 |
5 |
|
16 |
Iron / Steel / Kerosene Stoves |
18.5 |
5 |
|
17 |
Sand Lime Bricks |
6 |
5 |
|
18 |
Peat |
19.5 |
5 |
|
19 |
All Ores and Concentrates |
18.5 |
5 |
|
20 |
Kerosene PDS |
17 |
5 |
|
21 |
Tar |
12 |
5 |
|
22 |
Coal |
12 |
5 |
|
23 |
Lignite |
12 |
5 |
|
24 |
Braille Typewriters |
13.5 |
5 |
|
25 |
Animal or Human Blood Vaccines |
6 |
5 |
|
26 |
Sand Lime Bricks, Fly Ash Bricks |
6 |
5 |
|
27 |
Geometry Box |
18.5 |
5 |
|
28 |
Pencil Sharpeners, Knives |
18.5 |
12 |
|
29 |
Meat & Fish Preparations |
19.5 |
12 |
|
30 |
Candles |
26 |
12 |
|
31 |
Tooth Powder |
26 |
12 |
|
32 |
LED Lights |
26 |
12 |
|
33 |
Milk Beverages |
26 |
12 |
|
34 |
Ready to Eat Namkeen/Bhujia |
26 |
12 |
|
35 |
Sports Goods |
18.5 |
12 |
|
36 |
Bicycles |
18.5 |
12 |
|
37 |
Spectacle Lens |
18.5 |
12 |
|
38 |
Aluminium Utensils |
18.5 |
12 |
|
39 |
Power Driven Water Pumps |
12.5 |
12 |
|
40 |
Fertilizers |
18.5 |
12 |
|
41 |
Tractors |
18.5 |
12 |
|
42 |
Sewing / Knitting Needles |
18.5 |
12 |
|
43 |
Works Contracts |
15 |
12 |
|
44 |
Non AC / Alcohol Serving Restaurants |
13-14 |
12 |
|
45 |
Aluminium Foil |
18.5 |
18 |
|
46 |
Infant Use Preparations |
19.5 |
18 |
|
47 |
Pasta, Corn Flakes and Cakes |
19.5 |
18 |
|
48 |
Condensed Milk |
18.5 |
18 |
|
49 |
Toilet Paper |
18.5 |
18 |
|
50 |
Hot Water Bottles |
18.5 |
18 |
|
51 |
Petroleum Jelly, Paraffin Wax |
20 |
18 |
|
52 |
Ice cream, Instant Food Mixes, Sharbet |
26 |
18 |
|
53 |
Refined Sugar |
26 |
18 |
|
54 |
Soap |
26 |
18 |
|
55 |
Dentrifices - Toothpaste |
26 |
18 |
|
56 |
Hair Oil |
26 |
18 |
|
57 |
Whey Proteins & Fitness Supplements |
26 |
18 |
|
58 |
Hat and Other Headgears |
26 |
18 |
|
59 |
Printers |
26 |
18 |
|
60 |
Petroleum Coke, Petroleum Bitumen |
27.5 |
18 |
|
61 |
Copper Bars, Rods, Wires |
18.5 |
18 |
|
62 |
Copper Screws, Nuts, Bolts |
18.5 |
18 |
|
63 |
Nickel Bars, Rods, Wires |
18.5 |
18 |
|
64 |
Nickel Screw, Nuts, Bolts |
18.5 |
18 |
|
65 |
Nickel Tubes, Pipes, Netting |
18.5 |
18 |
|
66 |
Aluminium Ingots, Rods, Wires |
18.5 |
18 |
|
67 |
Lead Plates, Sheets, Strips |
18.5 |
18 |
|
68 |
Zinc Goods |
18.5 |
18 |
|
69 |
Tin Bars, Rods |
18.5 |
18 |
|
70 |
Padlocks, Locks |
18.5 |
18 |
|
71 |
Helmets |
18.5 |
18 |
|
72 |
Plastic Products |
18.5 |
18 |
|
73 |
AC, Alcohol Serving Restaurants |
22 |
18 |
|
74 |
Cement |
30 |
28 |
Related Posts:
Which products and services have become costlier after GST roll out?